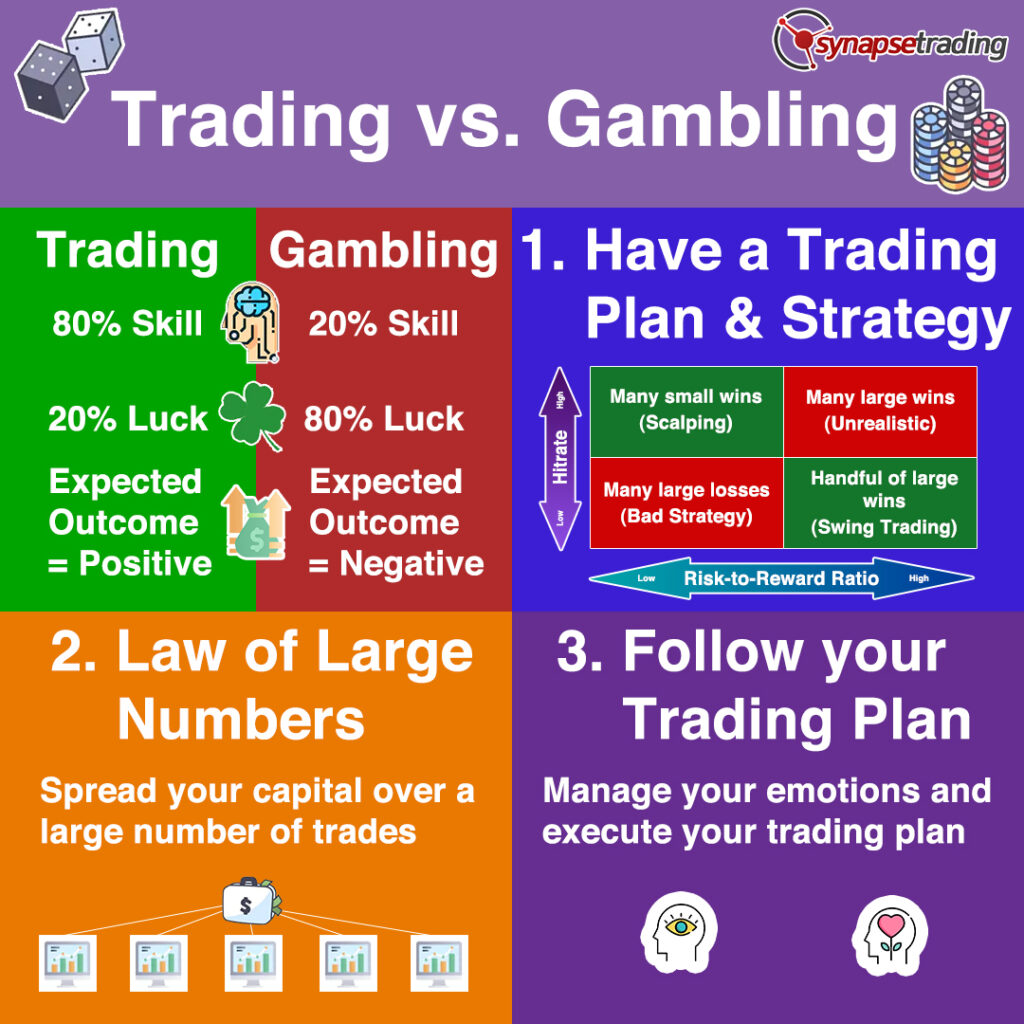
The financial world is often misunderstood, and for many, it can seem like a high-risk game where luck plays a major role. Forex trading, the global exchange of currencies, is sometimes likened to gambling because of its speculative nature. However, beneath the surface, these two activities are driven by very different principles. While gambling relies on chance, forex trading is a strategic, skill-based activity grounded in analysis, market behavior, and risk management.
Check out» Bitcoin Price Today
In this article, we will break down these differences, exploring how forex trading works, why it is not the same as gambling, and how you can avoid the pitfalls of speculative behavior. Whether you are a seasoned trader or just starting to explore the forex market, understanding the distinction between trading and gambling is crucial for long-term success.
Forex Trading Versus Gambling
Forex trading and gambling share some similarities, but they are fundamentally different in key ways.
Here’s how they compare:
Similarities:
-
Risk Involvement: Both involve the risk of losing money.
-
Uncertainty: Future outcomes in both activities are uncertain.
-
Short-Term Gains & Losses: Both can result in quick profits or losses.
Differences:
| Aspect | Forex Trading | Gambling |
|---|---|---|
| Skill vs. Luck | Involves analysis, strategy, and risk management. | Mostly based on chance (except in skill-based games like poker). |
| Long-Term Viability | Profitable traders rely on strategy and risk management. | The house (casino) always has the edge in the long run. |
| Market Influence | External factors like economics, politics, and news affect forex prices. | The outcome is usually independent of external events. |
| Risk Control | Traders can use stop-loss, risk-reward ratios, and analysis to manage risk. | Once money is bet, control over the outcome is minimal. |
| Investment Mindset | Treated as a business with analysis, patience, and discipline. | Typically involves quick wins/losses without strategic planning. |
Bottom Line:
-
Forex trading is not gambling if done correctly, using proper analysis, risk management, and strategy.
-
However, if someone trades without knowledge or discipline, purely relying on luck, then it becomes gambling.
How to trade forex wisely
1️⃣ Understanding the Forex Market
Forex (foreign exchange) trading involves buying one currency while selling another. The goal is to profit from price movements.
-
Major Pairs: EUR/USD, GBP/USD, USD/JPY, etc.
-
Market Hours: Open 24/5, with key sessions (London, New York, Tokyo).
2️⃣ Key Concepts in Forex Trading
✅ Currency Pairs:
-
Every forex trade involves two currencies (e.g., EUR/USD).
-
The first currency (EUR) is the base currency, and the second (USD) is the quote currency.
-
If EUR/USD = 1.1000, it means 1 EUR = 1.10 USD.
✅ Bid & Ask Price:
-
Bid price: The price at which you can sell a currency.
-
Ask price: The price at which you can buy a currency.
-
The difference between them is called the spread (broker’s fee).
✅ Pips & Lots:
-
A pip (percentage in point) is the smallest price movement (usually 0.0001 for most pairs).
-
Trades are measured in lots:
-
Standard lot = 100,000 units
-
Mini lot = 10,000 units
-
Micro lot = 1,000 units
-
✅ Leverage & Margin:
-
Leverage allows you to control a larger position with less money.
-
Example: With 1:100 leverage, $100 can control $10,000 worth of currency.
-
Margin is the amount of money required to keep a trade open.
3️⃣ How a Forex Trade Works
Here’s a simple example to help you understand the mechanics:
Example: EUR/USD Trade
-
Current Price: EUR/USD = 1.1000 (This means 1 Euro = 1.10 USD)
-
You Buy EUR/USD:
-
You believe the Euro will increase in value relative to the Dollar.
-
Let’s say you buy 1 standard lot (100,000 units of EUR).
-
You are buying 100,000 Euros, and your cost is 1.1000 * 100,000 = $110,000.
-
-
Price Moves Up (You Profit):
-
A few hours later, the EUR/USD price moves to 1.1050.
-
You sell the 100,000 Euros at this new price.
-
Sell Price: 1.1050
-
You receive 1.1050 * 100,000 = $110,500 (your selling price).
-
Profit: $110,500 – $110,000 = $500
-
-
Price Moves Down (You Lose):
-
If the price moves in the opposite direction and drops to 1.0950, you sell the 100,000 Euros for only $109,500.
-
Loss: $110,000 – $109,500 = $500
-
Key Takeaways:
-
Pip Movement: The price movement between 1.1000 and 1.1050 is 50 pips.
-
Profit/Loss: Since you traded 1 standard lot (100,000 units), each pip movement is worth $10. So, 50 pips = $500 profit/loss.
4️⃣ Risk Management in Forex Trading
1. Position Sizing
Position sizing refers to how much of your account balance you risk on each trade. It’s essential to limit your exposure to avoid large losses.
-
Risk per trade: A common guideline is to risk 1-2% of your capital on each trade.
-
Example: If you have a $10,000 account, you might risk $100-$200 per trade.
-
To calculate position size:
Position size=Amount to riskStop loss in pips×Value of one pip\text{Position size} = \frac{\text{Amount to risk}}{\text{Stop loss in pips} \times \text{Value of one pip}}
2. Stop-Loss Orders
A stop-loss is a predetermined price where your position will be automatically closed to limit your losses.
-
Example: If you set a stop-loss 50 pips below your entry price, and each pip is worth $10, your maximum loss would be $500 if the market moves against you.
3. Risk-Reward Ratio
The risk-reward ratio helps you evaluate if a trade is worth taking.
-
A good risk-reward ratio is typically 1:2 or higher. This means that for every dollar you risk, you aim to make at least two dollars in profit.
-
Example: If you risk $100, you should aim for a profit of $200.
4. Take-Profit Orders
A take-profit is the opposite of a stop-loss. It automatically closes your trade when the price reaches a specified level, locking in your profit.
-
Example: If you believe EUR/USD will rise to 1.1050, you can set a take-profit at that level to secure your gains.
5. Avoiding Overtrading
Overtrading occurs when you take too many trades or risk too much of your capital. This increases the chances of large losses and quickly depletes your account.
-
Key Tip: Stick to your trading plan and avoid getting emotional, especially after a series of wins or losses.
6. Use of Leverage
While leverage can amplify gains, it also magnifies losses.
-
Tip: Use leverage cautiously—starting with lower leverage, like 1:10 or 1:20, is safer until you gain more experience.
5️⃣ Trading Strategies
Now that you have the basics, let’s look at a few common trading strategies:
1. Trend Following
This strategy involves identifying the market trend (up or down) and trading in the direction of that trend.
-
Tools: Moving Averages (e.g., 50-period, 200-period).
-
How it works: Buy when the price is above the moving average (indicating an uptrend) and sell when the price is below (indicating a downtrend).
2. Breakout Trading
A breakout occurs when the price moves beyond a well-established support or resistance level.
-
How it works: You place a trade when the price breaks through a significant level, expecting it to continue in that direction.
3. Range Trading
Range trading involves identifying levels of support and resistance where the price tends to bounce back and forth within a certain range.
-
How it works: Buy at support and sell at resistance.
4. Scalping
Scalping is a very short-term strategy where you make small profits from quick, small price movements.
-
How it works: You open and close trades within minutes or even seconds, aiming for small profits.
5. News Trading
News events like economic data releases or geopolitical events can create significant price movements.
-
How it works: You trade based on expected reactions to news announcements, but it’s risky since the market can move unpredictably.
6️⃣ Psychology of Trading
The mental aspect of trading is just as important as strategy and risk management. Successful traders are disciplined and emotional control is key.
-
Patience: Wait for good setups and don’t rush into trades.
-
Discipline: Stick to your trading plan, even during losses.
-
Emotional Control: Avoid overreacting to a win or loss. Keep a clear mindset and don’t trade based on emotions like fear or greed.
7️⃣ Paper Trading (Practice)
Before diving into real money trading, paper trading is a great way to practice strategies without risk.
-
Use a demo account from a broker to simulate real trading conditions.
-
Track your results, refine your strategies, and build confidence.
Next Steps
-
Choose a strategy that suits your personality.
-
Develop a trading plan (rules for entry, exit, and risk management).
-
Start small and use a demo account to practice.
8️⃣ Setting Up Your Trading Platform
Most forex brokers provide MetaTrader 4 (MT4) or MetaTrader 5 (MT5) as their primary trading platforms. These platforms are popular because they offer a wide range of tools and features for analysis and trading. Here’s how to get started:
1. Choose a Broker and Open an Account
-
Research Brokers: Look for a regulated broker with a good reputation. Ensure that they offer competitive spreads, good customer service, and suitable leverage options.
-
Account Type: Brokers offer different account types (Standard, ECN, or STP). Choose one based on your trading needs.
2. Download and Install MetaTrader
-
Most brokers allow you to download MT4 or MT5 directly from their website. Install it on your computer or mobile device.
3. Fund Your Account
-
After registration, fund your account using one of the available payment methods (e.g., bank transfer, credit card, or e-wallets).
4. Set Up Your Chart and Indicators
Once you’ve logged into the platform, here’s how to set it up:
-
Chart Setup:
-
Choose your desired currency pair from the Market Watch list.
-
Open a new chart for that pair.
-
Adjust timeframes (1m, 5m, 1h, etc.) to match your trading style.
-
-
Indicators:
-
Moving Averages: Add a moving average to track trends.
-
RSI (Relative Strength Index): Helps you identify overbought or oversold conditions.
-
MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): Helps you spot potential price reversals.
-
-
Support/Resistance Levels: Manually draw horizontal lines where the price has bounced before to identify key levels.
5. Start with a Demo Account
Before risking real money, practice on a demo account. This will help you get used to:
-
Platform Navigation
-
Setting Stop-Loss/Take-Profit
-
Placing Orders (Market Orders, Limit Orders, Stop Orders)
9️⃣ Developing a Trading Plan
A solid trading plan is essential for consistent success. Here’s how to structure one:
1. Define Your Goals
-
Short-term goals: Focus on learning the basics, developing a strategy, and understanding the platform.
-
Long-term goals: Aim for consistent profitability, ideally growing your capital by 10-20% annually (depending on your risk tolerance).
2. Set Risk Parameters
-
Risk per Trade: Stick to your risk management rules (1-2% per trade).
-
Max Drawdown: Decide the maximum loss you are willing to accept (e.g., a 10% drawdown means you stop trading to reassess).
3. Choose Your Trading Strategy
-
Based on your goals, choose a strategy (e.g., trend following, range trading, scalping, etc.).
-
Define entry and exit criteria: What will trigger you to enter or exit a trade?
-
For example, enter a long position when the price is above a 50-period moving average and the RSI is below 30 (indicating oversold conditions).
-
4. Set Trading Hours
-
When to Trade: Define the times you will trade (e.g., during London or New York session).
-
Avoid Trading During News Events: Major economic releases or geopolitical events can cause volatility. It’s often best to stay out of the market during these periods until you understand the news’ impact.
5. Keep a Trading Journal
-
Track Your Trades: Keep detailed records of every trade, including:
-
Trade entry and exit points
-
The reason for the trade
-
Risk-reward ratio and actual result
-
-
A journal will help you evaluate what’s working, what’s not, and adjust your strategy over time.
🔟 Tips for Successful Forex Trading
Here are a few key tips to help you succeed in the long run:
1. Start Small
-
When you start live trading, only risk a small percentage of your capital (1-2% per trade).
-
Begin with micro lots or mini lots to minimize your exposure while learning.
2. Focus on One or Two Currency Pairs
-
Initially, focus on 1-2 pairs (e.g., EUR/USD and GBP/USD). This allows you to better understand their movements and behavior without being overwhelmed by too many options.
3. Avoid Overleverage
-
While leverage can amplify your gains, it can also lead to large losses. Use lower leverage (e.g., 1:10 or 1:20) to manage your risk better.
4. Stay Updated with Market News
-
Economic indicators (like GDP, inflation, unemployment) and political events (like elections or central bank policies) can significantly affect currency prices.
-
Subscribe to financial news websites like Bloomberg, Reuters, or CNBC.
5. Don’t Chase the Market
-
Avoid jumping into trades out of FOMO (Fear of Missing Out). Wait for the right setups and follow your plan.
-
Sometimes, the best trade is no trade.
6. Be Prepared for Drawdowns
-
Losses are a part of trading. No trader wins 100% of the time.
-
Focus on consistent, small gains rather than seeking big wins on every trade.
7. Keep Learning
-
Forex trading is an ongoing learning process. Read books, watch videos, attend webinars, and follow successful traders to expand your knowledge.
-
Popular Books:
-
“Trading in the Zone” by Mark Douglas
-
“The Little Book of Currency Trading” by Kathy Lien
-
“Market Wizards” by Jack Schwager
-
11️⃣ Evaluating Your Performance
Periodically assess your trading performance:
-
Review your winning and losing trades to spot patterns and areas of improvement.
-
Use tools like myfxbook to track your performance and stats.
-
Adjust your strategies and goals based on your performance and market conditions.
Final Thoughts
Forex trading isn’t a get-rich-quick endeavor. It requires patience, discipline, and continuous learning. If you stick to a solid plan, manage your risks, and stay disciplined, you’ll improve your chances of success.
1️⃣ Advanced Forex Strategies
1.1. Carry Trade Strategy
A carry trade involves borrowing money in a currency with a low interest rate and investing in a currency with a higher interest rate.
-
How it works: You profit from the difference in interest rates, known as the interest rate differential.
-
Example:
-
Borrow Japanese yen (JPY), which has low interest rates.
-
Use the funds to buy Australian dollars (AUD), which have higher interest rates.
-
The idea is to earn the interest on the AUD while also potentially benefiting from price movement.
-
Important Considerations:
-
Be cautious of currency volatility. A sudden shift in currency values can outweigh interest gains.
-
Carry trades typically work well in stable market conditions.
1.2. Fibonacci Retracement Strategy
Fibonacci retracement levels help identify potential areas of support and resistance.
-
Key Levels: 23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, 78.6% (with 61.8% being the most important).
-
How it works:
-
You identify a strong price movement (up or down).
-
Then, use Fibonacci retracement to predict potential pullback levels (price corrections) before the trend continues.
-
Traders buy at the key support levels during an uptrend or sell at resistance during a downtrend.
-
1.3. Price Action Trading
Price action trading involves making decisions based on the actual movement of the market, rather than using indicators. It focuses on candlestick patterns, support and resistance, and trendlines.
-
Candlestick Patterns: Look for bullish or bearish engulfing patterns, doji candles, and pin bars to predict potential reversals.
-
Trendlines: Draw trendlines connecting key highs and lows. Buy when the price is near the support trendline in an uptrend and sell when near the resistance trendline in a downtrend.
Key Benefit:
-
Price action is a more pure form of trading that relies on real-time market data.
2️⃣ Popular Chart Patterns
Chart patterns are useful tools for predicting future price movements based on historical price action. Here are some of the most common and reliable patterns to recognize:
2.1. Head and Shoulders
-
Formation:
-
In an uptrend, a head and shoulders pattern forms when the price creates three peaks: a higher peak (head) between two smaller peaks (shoulders).
-
In a downtrend, the opposite pattern (inverse head and shoulders) can occur.
-
-
Signal: The breakout from the neckline (a horizontal support or resistance line) is seen as a strong signal to enter a trade in the opposite direction of the trend.
Example:
-
In an uptrend: The breakout below the neckline signals a reversal to a downtrend.
-
In a downtrend: The breakout above the neckline signals a reversal to an uptrend.
2.2. Double Top and Double Bottom
-
Double Top: A bearish reversal pattern that occurs after an uptrend. It forms two peaks at roughly the same level, with a dip in between.
-
Entry: Short when the price breaks below the support level formed between the two tops.
-
-
Double Bottom: A bullish reversal pattern that occurs after a downtrend. It forms two troughs at roughly the same level, with a rise in between.
-
Entry: Buy when the price breaks above the resistance level formed between the two bottoms.
-
2.3. Triangle Patterns
-
Symmetrical Triangle: This pattern forms when the price is squeezed between converging trendlines, with lower highs and higher lows.
-
Breakout: The breakout can occur either up or down, and is typically in the direction of the prior trend.
-
-
Ascending Triangle: This is a bullish pattern formed by a horizontal resistance line and an ascending support line.
-
Breakout: The breakout typically happens upward.
-
-
Descending Triangle: This is a bearish pattern formed by a horizontal support line and a descending resistance line.
-
Breakout: The breakout typically happens downward.
-
2.4. Flags and Pennants
-
These are continuation patterns that occur after a strong price movement, followed by a consolidation period.
-
Flags: A flag looks like a small rectangle or parallelogram that slopes against the prevailing trend.
-
Pennants: A pennant looks like a small triangle and is similar to a symmetrical triangle but with a shorter consolidation period.
Entry: After the consolidation, traders often wait for the breakout in the direction of the prevailing trend.
3️⃣ Combining Strategies and Patterns
The key to becoming a successful trader is combining strategies and patterns to increase your chances of a favorable outcome. Here are a few ways to do this:
3.1. Trend + Support/Resistance
-
Identify the overall trend (using moving averages, for example).
-
Use support and resistance levels to time your entries.
-
In an uptrend, buy when the price pulls back to support.
-
In a downtrend, sell when the price bounces down from resistance.
-
3.2. Combining Indicators
-
Use RSI and MACD together to confirm entries. For example, you could buy when RSI is oversold (below 30) and the MACD crosses above its signal line.
-
Combine Fibonacci retracement levels with candlestick patterns to confirm potential reversal points.
3.3. Price Action + News Trading
-
Before entering a trade, check the economic calendar for major news events that might affect the currency pair you’re trading.
-
Use price action (candlestick patterns) around news events to gauge market sentiment.
4️⃣ Common Mistakes to Avoid
4.1. Ignoring Risk Management
-
Always use stop-loss orders to manage risk and protect your capital.
-
Never risk more than a small percentage of your trading account on a single trade (1-2%).
4.2. Overleveraging
-
High leverage can lead to significant losses. Only use leverage when you understand how it works, and always stay within your risk tolerance.
4.3. Lack of Discipline
-
Trading without a plan, chasing the market, or reacting emotionally can lead to impulsive decisions and unnecessary losses.
-
Stick to your trading plan and avoid trading when emotionally upset.
4.4. Failing to Keep a Trading Journal
-
Not tracking your trades means you’re missing out on valuable learning opportunities. Always analyze your past trades to improve your strategies.
Final Thoughts
By combining solid strategies, understanding key chart patterns, and practicing risk management, you can build a strong foundation in forex trading. It takes time and patience, but with practice, you can achieve consistent success.
5️⃣ Advanced Forex Tools and Concepts
Now that you have a solid understanding of trading strategies and chart patterns, let’s dive into some advanced tools and concepts that successful traders use to enhance their strategies.
5.1. MetaTrader Expert Advisors (EAs)
An Expert Advisor (EA) is an automated trading system that executes trades on your behalf based on predefined rules. They can:
-
Open and close trades.
-
Set stop-loss, take-profit, and trailing stop orders.
-
Monitor the market 24/7 without human intervention.
Pros of Using EAs:
-
They remove emotions from trading.
-
Can trade even when you’re away from your computer.
-
Great for backtesting strategies.
Cons:
-
Not foolproof: EAs can perform poorly in volatile or unpredictable markets.
-
Requires monitoring and regular updates to remain effective.
5.2. Backtesting Your Strategy
Backtesting involves testing a trading strategy using historical price data to see how it would have performed in the past.
-
Tools: You can use MetaTrader’s Strategy Tester to backtest your strategies.
-
Benefits:
-
Understand how a strategy performs over time.
-
Adjust your strategy based on past data to optimize future performance.
-
Steps for Backtesting:
-
Select a time period (months, years).
-
Choose the currency pair and timeframe.
-
Test your strategy using historical data.
-
Analyze the results: Win rate, risk-reward ratio, maximum drawdown, etc.
5.3. Trading with Correlations
Currency pairs have correlations with each other, meaning their price movements can be linked in various ways:
-
Positive Correlation (Direct Correlation): When two pairs move in the same direction. For example, EUR/USD and GBP/USD often move similarly.
-
Negative Correlation (Inverse Correlation): When two pairs move in opposite directions. For example, EUR/USD and USD/CHF typically have a negative correlation.
Using Correlations:
-
Hedging: You can hedge positions by trading two negatively correlated pairs (e.g., buying EUR/USD while selling USD/CHF).
-
Confirmation: If you’re unsure about a trade, you can use correlations to check if other pairs are moving similarly or in the opposite direction.
5.4. Volatility Indicators (ATR and VIX)
Volatility is a key factor in forex trading because it determines how far a price can move in a given period, influencing the potential for profits or losses.
-
Average True Range (ATR):
-
ATR measures market volatility. The higher the ATR, the more volatile the market is.
-
Use ATR to set your stop-loss based on volatility rather than a fixed number of pips.
-
-
VIX (Volatility Index):
-
While more common in equity markets, the VIX can be a useful gauge for understanding global market sentiment and risk.
-
When the VIX rises, it signals increased market fear and volatility, which can affect forex prices.
-
6️⃣ Risk Management Advanced Techniques
Managing risk is crucial for long-term success in forex trading. Let’s go beyond the basics and explore some advanced risk management techniques.
6.1. Position Sizing
Position sizing is a critical component of managing your risk and adjusting your exposure. You need to adjust the size of your trade based on your risk tolerance and stop-loss distance.
-
Formula for position size:
Position Size=Account RiskStop Loss in pips×Value of a pip\text{Position Size} = \frac{\text{Account Risk}}{\text{Stop Loss in pips} \times \text{Value of a pip}}
-
Example: If you have $1,000 in your account, you risk 2% ($20), and your stop-loss is 50 pips with a pip value of $1, your position size would be:
Position Size=2050×1=0.4 lots\text{Position Size} = \frac{20}{50 \times 1} = 0.4 \text{ lots}
-
6.2. Scaling In and Out of Trades
Scaling into a trade involves gradually increasing your position as the price moves in your favor.
-
Example: If you enter a trade with a small position and the price moves in your favor, you can add more positions (scaling in) to maximize potential profit.
-
Scaling out: The opposite strategy, where you reduce your position as the price moves in your favor to lock in profits.
Key Benefit: This allows for a more flexible risk management approach and enables you to take advantage of favorable market moves while reducing exposure if the market moves against you.
6.3. Dynamic Stop-Loss and Take-Profit
Instead of using fixed stop-loss and take-profit levels, you can use dynamic stops based on market conditions.
-
Trailing Stop: A trailing stop moves with the price in your favor, locking in profits as the price moves.
-
Example: You set a trailing stop of 30 pips. If the price moves 30 pips in your favor, the stop-loss is adjusted to lock in profits.
-
-
ATR-Based Stop: Adjust your stop-loss based on the Average True Range (ATR). This accounts for current market volatility and gives the trade more breathing room during volatile periods.
7️⃣ Monitoring Your Trading Performance
7.1. Performance Metrics
Track your trading performance with key metrics that give you a clear picture of how well you’re doing:
-
Win Rate: The percentage of profitable trades.
Win Rate=Number of Winning TradesTotal Number of Trades×100\text{Win Rate} = \frac{\text{Number of Winning Trades}}{\text{Total Number of Trades}} \times 100
-
Profit Factor: The ratio of gross profit to gross loss.
Profit Factor=Gross ProfitGross Loss\text{Profit Factor} = \frac{\text{Gross Profit}}{\text{Gross Loss}}
-
Risk-Reward Ratio: The ratio between the amount of risk you take versus the reward you aim for.
-
A risk-reward ratio of 1:2 means you’re risking $1 to make $2.
-
7.2. Regular Reviews
-
Weekly and Monthly Reviews: At the end of each week or month, review your trading journal and performance metrics.
-
Track Mistakes: Identify any recurring mistakes or emotional reactions and find ways to improve.
7.3. Improve Consistency
As you refine your strategies, focus on maintaining consistency. Avoid trying to “chase” profits by jumping between different strategies or taking impulsive trades.
8️⃣ Continuous Learning and Adaptation
The forex market is constantly changing, so it’s crucial to adapt and evolve your trading approach over time. Here are some ways to continue your learning journey:
8.1. Stay Updated with Market Trends
-
Read financial news from sources like Bloomberg, Reuters, and MarketWatch.
-
Keep an eye on central bank policies (like the Fed, ECB, and BoJ) as they significantly impact currency movements.
8.2. Join Trading Communities
-
Forums: Participate in online trading forums and communities to learn from others. Websites like BabyPips and Trade2Win have active communities where traders share ideas.
-
Social Trading: Some platforms allow you to copy the trades of more experienced traders, learning from their strategies in real-time.
8.3. Take Advanced Courses or Mentorship
-
Consider enrolling in advanced trading courses or finding a mentor who can guide you through complex strategies.
-
Trading psychology courses can help you maintain emotional control during tough market conditions.
Final Thoughts
Mastering forex trading is a continuous journey. With advanced tools, effective risk management, and constant learning, you can significantly improve your trading performance. The most important aspect is developing your personal trading strategy that suits your risk tolerance, time availability, and trading style.
Highlights of This Article
-
Forex Trading vs Gambling:
We began by exploring the key differences between forex trading and gambling. Unlike gambling, where the outcome is based on luck, forex trading involves analysis, strategies, and risk management. Success in forex trading is achievable through careful planning, discipline, and market knowledge. Gambling, on the other hand, is driven by chance without any substantial analysis or skill-based approach. -
Understanding Forex Market Basics:
We then delved into the fundamentals of the forex market, discussing the key concepts such as currency pairs, buying and selling currencies, and the importance of understanding trends.-
Major pairs and minor pairs were introduced, explaining how different currencies are traded in the global forex market.
-
-
Forex Trading Strategies:
Various trading strategies were covered, from day trading to scalping, swing trading, and position trading. We also highlighted the importance of choosing the right strategy based on your time availability and risk tolerance. -
Advanced Trading Techniques:
We explored carry trading, Fibonacci retracement, price action, and other technical tools that traders use to gain insights into market behavior. The focus was on understanding how to use these advanced strategies effectively. -
Chart Patterns and Technical Analysis:
We discussed popular chart patterns like head and shoulders, double tops/bottoms, and triangle patterns. The importance of recognizing these patterns to predict market moves was emphasized. -
Risk Management and Position Sizing:
Effective risk management is key to long-term success. We learned how to calculate position sizes based on your risk tolerance, understand the concept of dynamic stop-losses, and implement strategies like scaling in and out of trades. -
Trading Tools and Automation:
Tools like Expert Advisors (EAs), MetaTrader, and the use of backtesting were discussed as ways to automate trading and test strategies over historical data to understand their effectiveness. -
Risk Management Advanced Techniques:
We went over more advanced techniques, such as scaling in/out of positions, position sizing, and using ATR-based stops for better risk control. Understanding and managing volatility through tools like ATR and VIX were also covered. -
Tracking Performance and Reviewing Trades:
The importance of keeping a trading journal and reviewing your performance through key metrics such as win rate, risk-reward ratio, and profit factor was highlighted. -
Continuous Learning and Adaptation:
Finally, we emphasized that trading is an evolving skill, and it’s essential to stay updated with market trends, participate in trading communities, and take courses to enhance your knowledge and performance over time.
Conclusion
In conclusion, forex trading and gambling are fundamentally different in terms of strategy, analysis, and long-term success. Forex trading is a skill-based endeavor that relies on research, analysis, and risk management, while gambling is primarily driven by luck. Through understanding the core concepts of forex, applying effective trading strategies, and using advanced tools, traders can increase their chances of success.
The journey of becoming a proficient forex trader involves:
-
Developing discipline and following a structured trading plan.
-
Implementing strong risk management practices to protect capital.
-
Utilizing technical analysis and chart patterns to predict market behavior.
-
Leveraging advanced tools like Expert Advisors and backtesting to automate and optimize your trading strategy.
Additionally, by consistently reviewing performance, keeping a trading journal, and adapting strategies to market conditions, traders can continuously improve. Mastery of forex trading requires time, experience, and a commitment to learning.
In essence, forex trading is not a get-rich-quick scheme, but a path that demands careful planning, patience, and perseverance. With the right mindset and tools, anyone can become a successful forex trader over time. Stay disciplined, keep learning, and manage risks effectively to build a sustainable trading career.